Table of contents
In the last blog of day18, we saw the benefits of using docker compose and how we can use it to create multiple containers at once. Today, we will see how we can mount disk spaces (which can be used as storage facilities for docker containers) and how to connect docker containers to provide a complete service.
A line from my last blog mentioned using a mountable volume that can be used as a storage space for docker containers. Let's see how we can do exactly that!
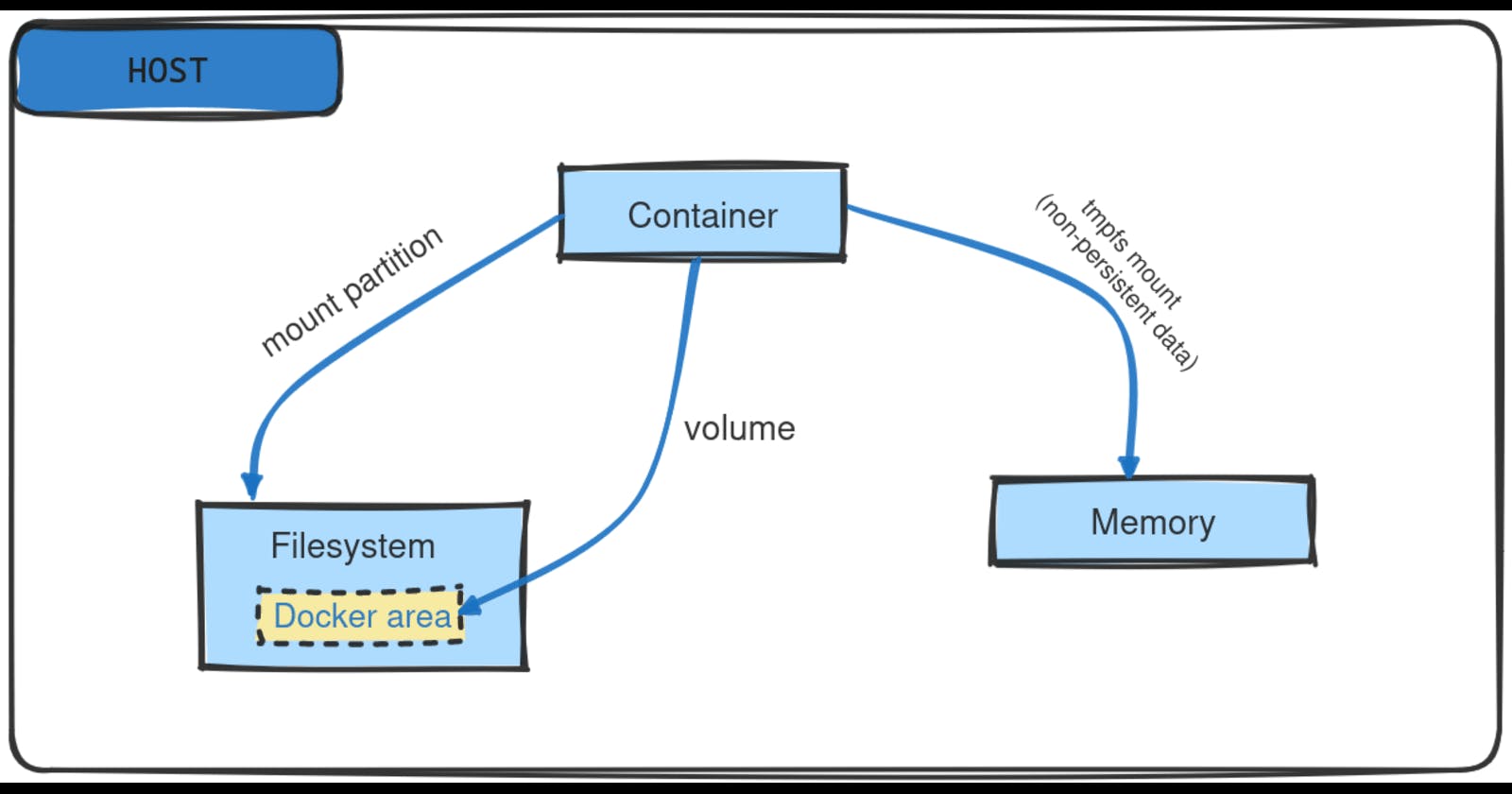
Docker Volume
It can be thought of as the persistent storage space for the container data.
Volumes continue to exist even after the container associated with it is removed or deleted; i.e. docker volumes need to be explicitly deleted.
Volumes are generally used as databases or storage areas for docker containers.
Two or more containers can also use the same volume. This is generally required if data needs to be shared among the containers.
A thoughtful scenario...
How do I export the contents of a docker volume to another host?
One practical solution I see goes like this:
Backup the contents of volumes.
Restore this backup on the new host.
Run the docker-compose files on the new machine.
Thus, recreate the contianers on the new system along with the volume contents.
Docker Network
This is taken care of by a networking system of Docker itself, to manage communications between contianers, the host and the outside world.
Creating docker network
docker network create -d <network_driver> <network_name>
The network drivers are as follows :
| Driver | Description |
| bridge | The default network driver. |
| host | Remove network isolation between the container and the Docker host |
| none | Completely isolate a container from the host and other containers |
| overlay | Overlay networks connect multiple Docker daemons together. |
| ipvlan | IPvlan networks provide full control over both IPv4 and IPv6 addressing |
| macvlan | Assign a MAC address to a container |
Task-1

Running the docker-compose file in detached mode
In the below file, I have only added the volumes section to the docker-compose file from day 18.
version: '3.1'
services:
mongo:
image: mongo
restart: always
environment:
MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_USERNAME: root
MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_PASSWORD: example
volumes:
- ./mongo-data:/data/db
# Mount a local directory './mongo-data' to the container's '/data/db' directory.
mongo-express:
image: mongo-express
restart: always
ports:
- 8081:8081
environment:
ME_CONFIG_MONGODB_ADMINUSERNAME: root
ME_CONFIG_MONGODB_ADMINPASSWORD: example
ME_CONFIG_MONGODB_URL: mongodb://root:example@mongo:27017/

Here's the output where the volume is created and data is stored in the mongo-data folder.

The list of running containers using docker ps :

Scale up or down the number of instances :
docker-compose up -d --scale mongodb=2

List and inspect the mounted volumes
docker volume ls
docker inspect $(docker volume ls)

Check logs
Enter the command to check logs of the running containers and the network :
docker-compose logs
View status of all containers started using docker-compose
docker-compose ps

Stopping and removing docker-compose entities
docker-compose down

Task-2

Name a docker volume and share files between multiple containers
docker volume create --name <any_name> --opt type=none --opt device=<path_to_mounting_area> --opt o=bind

You can check if multiple containers are sharing the same volume from the "Mounts" field in the docker inspect <container_name> .
Check if the contents are the same in the containers
docker exec <container_name1> ls /data/db
docker exec <container_name2> ls /data/db
List all volumes and remove them after use
docker volume ls
docker volume rm $(docker volume ls -q)